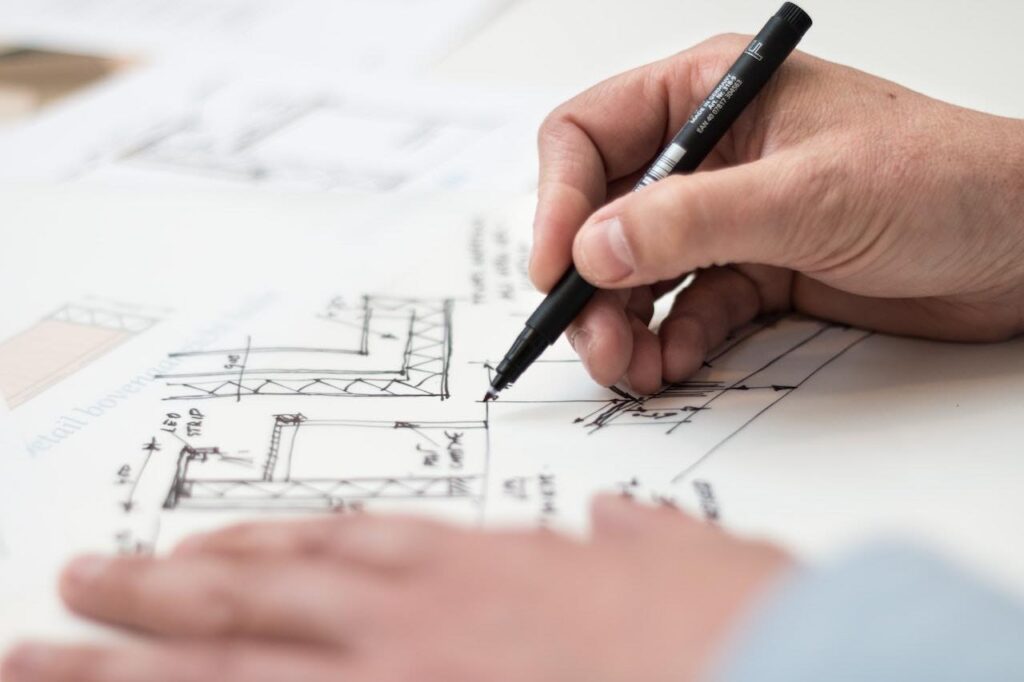

The process of manufacturing a new product is complex and involves several distinct stages. Each phase is critical to the success of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for companies and individuals seeking to bring innovative ideas to market. Here is some information about new product manufacturing and how it can be broken down into seven key stages. By gaining insight into this process, you can navigate the challenges, make informed decisions, and ultimately bring your product from concept to reality with confidence.
1. Conceptualization and Design
New product manufacturing begins with the conceptualization and design stage. This is where your innovative ideas take shape. Product designers and engineers work together to create detailed plans, sketches, and prototypes, outlining the product’s form, function, and features. These initial blueprints serve as the foundation for the entire manufacturing process.
In this phase, it’s essential to consider factors such as materials, production methods, and cost implications. Thoroughly reviewing your designs and making necessary adjustments is crucial to ensure the manufacturability of your product. Additionally, regulatory requirements and safety standards must be taken into account at this early stage to prevent potential roadblocks later in the process.
2. Prototyping and Testing
With the initial designs in place, the next stage involves creating prototypes and conducting rigorous testing. Prototyping allows you to assess the practicality of your design and make any necessary refinements. Prototypes can be created from your design with low-volume injection molding. Testing helps identify potential flaws and weaknesses, ensuring the final product meets quality and performance standards.
During this phase, it’s common to iterate on the design, testing multiple versions of the product to refine its functionality and durability. Collaborate closely with product testers and engineers to gather valuable feedback. The goal is to iron out any kinks, confirm that the product functions as intended, and identify areas for improvement before moving on to mass production.
3. Material Sourcing and Supplier Selection
Material sourcing and supplier selection are critical stages in the manufacturing process. Once you have a refined design and a tested prototype, you need to secure the necessary materials for production. This involves identifying reliable suppliers and negotiating terms for procurement.
Choosing the right materials is critical as it impacts the quality, cost, and performance of your product. In addition, establishing strong relationships with suppliers is essential for consistent and timely material delivery. Consider factors such as material cost, availability, lead times, and supplier reliability when making your selections. Building a robust supply chain is crucial for a smooth manufacturing process.
4. Tooling and Manufacturing Setup
At this stage, the focus shifts to tooling and the setup of manufacturing facilities. Tooling involves the creation of molds, dies, and other production equipment necessary to produce the product at scale. This phase requires meticulous precision, as any errors can lead to defects in the final product.
The manufacturing setup involves configuring production lines, assembling machinery, and implementing quality control processes. This stage is essential for ensuring that the manufacturing process is efficient, consistent, and capable of meeting production targets. Attention to detail in tooling and setup is vital for maintaining product quality and minimizing waste.
5. Mass Production
With everything in place, it’s time for mass production to begin. This stage involves producing the product on a large scale, meeting market demand, and fulfilling orders. Production efficiency, quality control, and adherence to safety standards are critical during mass production to ensure that the manufactured products are consistent and meet customer expectations.
Establishing a production schedule, monitoring inventory levels, and optimizing production flows are essential to minimize downtime and maintain cost-effectiveness. It’s also important to have quality control measures in place to detect and address any defects that may arise during mass production.
6. Quality Control and Assurance
Quality control and assurance is an ongoing process that runs parallel to mass production. This stage involves continuous monitoring and inspection of the manufactured products to ensure they meet the established quality standards. Any deviations or defects are identified, addressed, and corrected to maintain product integrity.
Quality control also encompasses compliance with industry regulations and safety standards. It’s imperative to have a quality management system in place to track product quality, manage defects, and maintain traceability. By implementing stringent quality control practices, you can minimize the likelihood of recalls and product defects reaching the market.
7. Packaging and Distribution
The final stage of new product manufacturing involves packaging and distribution. Products must be carefully packaged to protect them during transportation and storage. Effective packaging design not only ensures the product’s safety but also contributes to its marketability.
Distribution logistics include planning and executing the efficient movement of products from manufacturing facilities to distribution centers and, ultimately, to consumers. It’s vital to optimize supply chain and distribution processes to meet demand and minimize delays. Factors such as transportation methods, warehousing, and order fulfillment must be streamlined to ensure products reach customers promptly and in optimal condition.
Bottom Line
Understanding the stages of new product manufacturing is a fundamental aspect of successfully bringing innovative ideas to life. From the conceptualization and design phase to the final distribution of products, each stage plays a critical role in achieving a seamless manufacturing process. Understanding the challenges at each step allows you to make informed decisions. You can then mitigate potential obstacles and ultimately witness your product’s journey from concept to reality. This comprehensive understanding empowers manufacturers to create high-quality, market-ready products that leave a lasting impact on consumers and industries alike.















Leave a Reply